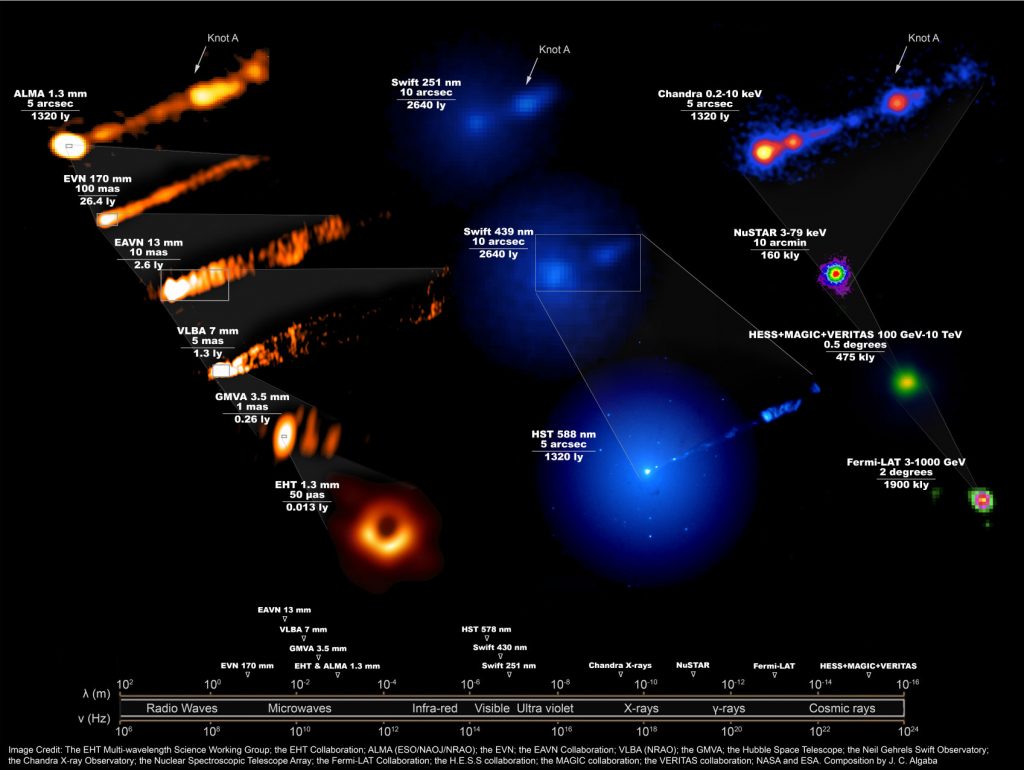
Credit: The EHT Multi-wavelength Science Working Group; the EHT Collaboration; ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO); the EVN; the EAVN Collaboration; VLBA (NRAO); the GMVA; the Hubble Space Telescope; the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory; the Chandra X-ray Observatory; the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array; the Fermi-LAT Collaboration; the H.E.S.S collaboration; the MAGIC collaboration; the VERITAS collaboration; NASA and ESA. Composition by J. C. Algaba
In April 2019, scientists released the first image of a black hole in the galaxy M87 using the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). However, that remarkable achievement was just the beginning of the science story to be told.
Data from 19 observatories are being released that promise to give unparalleled insight into this black hole and the system it powers, and to improve tests of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity.
“We knew that the first direct image of a black hole would be groundbreaking,” said Kazuhiro Hada of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, a co-author of a new study being published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters to describe the large set of data. “But to get the most out of this remarkable image, we need to know everything we can about the black hole’s behavior at that time by observing over the entire electromagnetic spectrum.”
The immense gravitational pull of a supermassive black hole can power jets of particles that travel at almost the speed of light across vast distances. M87’s jets produce light spanning the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to visible light to gamma rays. This pattern is different for each black hole. Identifying this pattern gives crucial insight into a black hole’s properties (for example, its spin and energy output), but this is a challenge because the pattern changes with time.
Scientists compensated for this variability by coordinating observations with many of the world’s most powerful telescopes on the ground and in space, collecting light from across the spectrum. This is the largest simultaneous observing campaign ever undertaken on a supermassive black hole with jets.
Beginning with the EHT’s now iconic image of M87, a new video takes viewers on a journey through the data from each telescope. Each consecutive frame shows data across many factors of ten in scale, both of wavelengths of light and physical size. The sequence begins with the EHT image of the black hole in M87 released in April 2019 (the data was obtained in April 2017). It then moves through images from other radio telescope arrays from around the globe, moving outward in the field of view during each step. (The scale for the width of squares is given in light years in the bottom right hand corner). Next, the view changes to telescopes that detect visible light (Hubble and Swift), ultraviolet light (Swift), and X-rays (Chandra and NuSTAR). The screen splits to show how these images, which cover the same amount of the sky at the same time, compare to one another. The sequence finishes by showing what gamma-ray telescopes on the ground, and Fermi in space, detect from this black hole and its jet.
Each telescope delivers different information about the behavior and impact of the 6.5-billion-solar-mass black hole at the center of M87, which is located about 55 million light-years from Earth.
“There are multiple groups eager to see if their models are a match for these rich observations, and we’re excited to see the whole community use this public data set to help us better understand the deep links between black holes and their jets,” said co-author Daryl Haggard of McGill University in Montreal, Canada.
The data were collected by a team of 760 scientists and engineers from nearly 200 institutions, spanning 32 countries or regions, and using observatories funded by agencies and institutions around the globe. The observations were concentrated from the end of March to the middle of April 2017.
The East Asian VLBI Network (EAVN), which is operated by NAOJ Mizusawa VLBI Observatory in collaboration with the Republic of Korea and China, also participated in this campaign to densely monitor the jets ejected from the black hole and record the dynamics of their structure and brightness. “In order to better understand the formation of black hole jets, one of the greatest mysteries in astronomy, quasi-simultaneous EAVN observations at the lower frequencies are unique to offer complementary information to properly interpret the EHT images, which bring us insights into the connections between the emission around the black hole itself and the jets at downstream,” says Yuzhu Cui, a Ph.D. student at the Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI) and a member of NAOJ Mizusawa VLBI Observatory, who led the analysis of the EAVN data. “This multi-wavelength research is a significant milestone which for the first time realized the joint observations at such a large scale in history.”
“This incredible set of observations includes many of the world’s best telescopes,” said co-author Juan Carlos Algaba of the University of Malaya in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. “This is a wonderful example of astronomers around the world working together in the pursuit of science.”
The first results show that the intensity of the light produced by material around M87’s supermassive black hole was the lowest that had ever been seen. This produced ideal conditions for viewing the ‘shadow’ of the black hole, as well as being able to isolate the light from regions close to the event horizon from those tens of thousands of light-years away from the black hole.
In order to understand the behavior around black holes during quiescence, the research team also conducted simulation and theoretical studies using NAOJ’s supercomputer dedicated to astronomy, “ATERUI II,” and compared the results with the multiwavelength observations. Based on a simple theoretical model, the team found that at least at the time of this observation, the gamma rays are being emitted in a different region than the radio emission region near the black hole observed by the EHT. “It has often been thought that radio waves and gamma rays are emitted from the same place,” says Tomohisa Kawashima, a research fellow at the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR), the University of Tokyo, who conducted the simulation using ATERUI II. “The simultaneous multiwavelength observations force us to rethink our conventional understandings, and it is expected that the theoretical and simulation studies in this field will develop rapidly in the future.”
The combination of data from these telescopes, and current (and future) EHT observations, will allow scientists to conduct important lines of investigation into some of astrophysics’ most significant and challenging fields of study. For example, scientists plan to use these data to improve tests of Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity. Currently, uncertainties about the material rotating around the black hole and being blasted away in jets, in particular the properties that determine the emitted light, represent a major hurdle for these GR tests.
A related question that is addressed by today’s study concerns the origin of energetic particles called “cosmic rays,” which continually bombard the Earth from outer space. Their energies can be a million times higher than what can be produced in the most powerful accelerator on Earth, the Large Hadron Collider. The huge jets launched from black holes, like the ones shown in today’s images, are thought to be the most likely source of the highest energy cosmic rays, but there are many questions about the details, including the precise locations where the particles get accelerated. Because cosmic rays produce light via their collisions, the highest-energy gamma rays can pinpoint this location, and the new study indicates that these gamma-rays are likely not produced near the event horizon—at least not in 2017. A key to settling this debate will be comparison to the observations from 2018, and the new data being collected this week.
“Understanding the particle acceleration is really central to our understanding of both the EHT image as well as the jets, in all their ‘colors’,” said co-author Sera Markoff, from the University of Amsterdam. “These jets manage to transport energy released by the black hole out to scales larger than the host galaxy, like a huge power cord. Our results will help us calculate the amount of power carried, and the effect the black hole’s jets have on its environment.”
The release of this new treasure trove of data coincides with the EHT’s 2021 observing run, which leverages a worldwide array of radio dishes, the first since 2018. Last year’s campaign was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the previous year was suspended because of unforeseen technical problems. This very week, EHT astronomers are targeting the supermassive black hole in M87 again, the one in our Galaxy (called Sagittarius A*), together with several more distant black holes for six nights. Compared to 2017 the array has been improved by adding three more radio telescopes: the Greenland Telescope, the Kitt Peak 12-meter Telescope in Arizona, and the NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA) in France.
“With the release of these data, combined with the resumption of observing and an improved EHT, we know many exciting new results are on the horizon,” said co-author Mislav Baloković of Yale University.
Additional Information
The Astrophysical Journal Letter describing these results is available here [https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/abef71]. This paper was led by 33 members of the EHT Multiwavelength Science Working Group, and includes as coauthors members of the following collaborations: the entire Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; the Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration; the H.E.S.S collaboration; the MAGIC collaboration; the VERITAS collaboration and the EAVN collaboration. The coordinators of the EHT Multiwavelength Science Working Group are Sera Markoff, Kazuhiro Hada, and Daryl Haggard, who together with Juan Carlos Algaba and Mislav Baloković, also coordinated work on the paper.
Partner MWL facilities include: European VLBI Network (EVN); High Sensitivity Array (HSA); VLBI Exploration of Radio Astrometry (VERA); Korea VLBI Network (KVN); East Asian VLBI Network/KVN and VERA Array (EAVN/KaVA); Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA); Global Millimeter VLBI Array (GMVA); Very Large Telescope Interferometer GRAVITY Instrument (VLTI/GRAVITY); Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory (Swift); Hubble Space Telescope (HST); Chandra X-ray Observatory (Chandra); Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR); High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission and X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission (XMM-Newton); Fermi Large Area Space Telescope (Fermi-LAT); High Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S.); Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes (MAGIC); Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System (VERITAS).
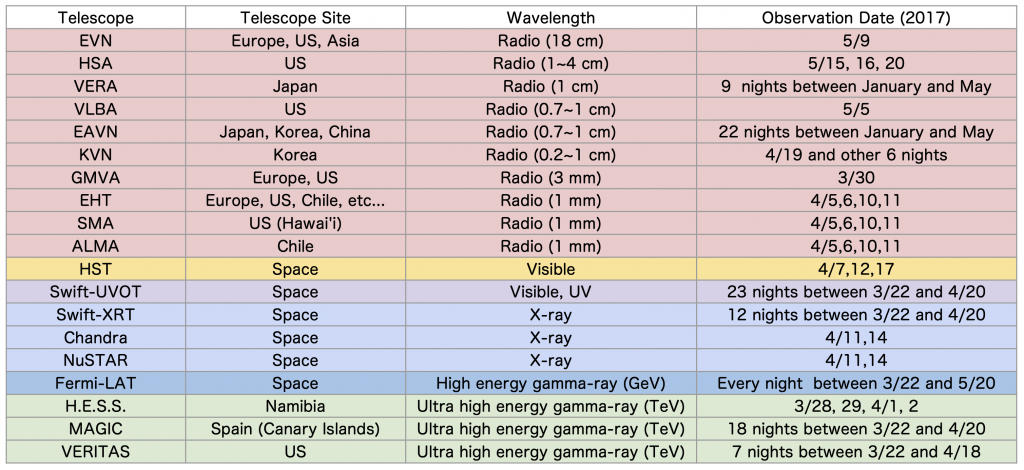
The 2017 campaign involved a large number of observatories and telescopes. At radio wavelengths it involved: the European Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) Network (EVN) on May 9, 2017; the High Sensitivity Array (HSA), which includes the Very Large Array (VLA), the Effelsberg 100m antenna and the 10 stations of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) on May 15, 16 and 20; the VLBI Exploration of Radio Astronomy (VERA) over 17 different times in 2017; the Korean VLBI Network (KVN) over seven epochs between March and December; the East Asian VLBI Network (EAVN) and the KVN and VERA Array (KaVA) , over 14 epochs between March and May 2017; the VLBA on May 5, 2017; the Global Millimeter-VLBI-Array (GMVA) on March 30, 2017; the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA); the Submillimeter Array (SMA) as part of an ongoing monitoring program. At ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths it involved the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory (Swift) with multiple observations between March 22 and April 20, 2017; and at optical wavelengths: Swift; and the Hubble Space Telescope on April 7, 12, and 17, 2017. (The Hubble data were retrieved from the Hubble archive because it was part of an independent observing program.) At X-ray wavelengths it involved the Chandra X-ray Observatory on April 11 and 14, 2017; the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) on April 11 and 14, 2017; and Swift. At gamma-ray wavelengths it involved Fermi from March 22 to April 20, 2017; the High Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S); the Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov (MAGIC) telescopes, and the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System (VERITAS).
The EHT Multi-wavelength (MWL) Working Group is a collective of EHT Collaboration members and external partners working together to ensure broadband MWL coverage during EHT campaigns, to maximize science output. The EHT collaboration involves more than 300 researchers from Africa, Asia, Europe, North and South America. The international collaboration is working to capture the most detailed black hole images ever obtained by creating a virtual Earth-sized telescope. Supported by considerable international investment, the EHT links existing telescopes using novel systems — creating a fundamentally new instrument with the highest angular resolving power that has yet been achieved.
The individual EHT telescopes involved are: ALMA, APEX, the IRAM 30-meter Telescope, the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT), the Large Millimeter Telescope (LMT), the Submillimeter Array (SMA), the Submillimeter Telescope (SMT), and the South Pole Telescope (SPT). The Greenland Telescope, the Kitt Peak Telescope, and NOEMA joined EHT after the 2017 observations. This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan / Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (Nos. 18KK0090, JP18K13594, JP18K03656, JP18H03721, 18K03709, 18H01245, 25120007, JP17J08829, JP19H01943, JP19H01908, JP19H01906), the National Institute of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan, the Toray Science Foundation,“Program for Promoting Researches on the Supercomputer Fugaku” (Toward a unified view of the universe: from large scale structures to planets), MEXT as “Priority Issue on post-K computer” (Elucidation of the Fundamental Laws and Evolution of the Universe) and JICFuS, and other funding agencies worldwide.
<Information of the paper>
Journal: Astrophysical Journal Letters
Title: “Broadband Multi-wavelength Properties of M87 During the 2017 Event Horizon Telescope Campaign”
Authors: Event Horizon Telescope Science Multi-Wavelength Science Working Group et al.