 Gravitational Wave Group
Gravitational Wave Group
Durability of the ultra-low loss mirror in the cryogenic environment.
 Motivation
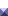
MotivationLCGT is characteristic to use cryogenic super-low loss mirrors as test masses of a Fabry-Perot type laser interferometer. Such mirrors, however, are worried to absorb molecules like a cryopump and to decrease their power reflection, which results in low cavity reflectance and low power recycling gain. In this experiment, we put a high-finesse Fabry-Perot cavity in a cryostat and monitored its finesse change for over one month to examine whether drastic contamination would take place or not.
Experimental setup
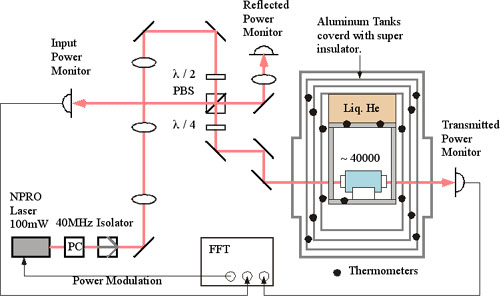
Clean room and housed cryostat

Optical setup
 Result(preliminary)
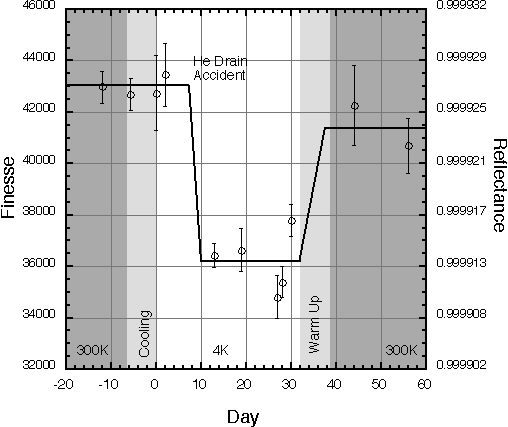
Result(preliminary)Remarkable finesse change at 4 [k] temperature and 10-7 [torr] vacuum level was not observed, exept for a change due to a low pressure (~10-3 [torr]) accident at 70[K] in 8th day. The finesse recover in 36th day was obtained just by heating up the whole system to 300[K]
 Next step
Next stepIn this expeiment, the 4[K] mirrors of the FP cavity are faced with each other, and the space betwen them was almost closed by a rod. In LCGT, each mirror faces with 300[K] vacuum and is expected to suffer from the 300[K] molecules attack. In the next step, finesse change of a FP cavity which is composed of one 4[k] mirror and one 300[K] mirror will be monitored.